Ten years of the KPMG CEO Outlook research shows CEO confidence in their organization’s future, with top CEOs navigating global turbulence by betting big on AI and talent.
From the race to embrace AI to ever-mounting geopolitical concerns, external challenges faced by today’s CEOs are vast and complex. At the same time, internal challenges such as upskilling the workforce and hybrid working are pushing CEOs to be agile and adaptable in their stakeholder management while also keeping an eye on longterm growth.
First launched 10 years ago, the KPMG CEO Outlook surveys more than 1,300 global business leaders overseeing companies with revenues of at least $500 million from some of the world’s biggest economies and key industries. Faced with a volatile global environment and unprecedented challenges over the past decade, top CEOs have remained resilient, leading their businesses on a path to sustainable growth in the face of declining confidence in the global economy.
Economic Outlook
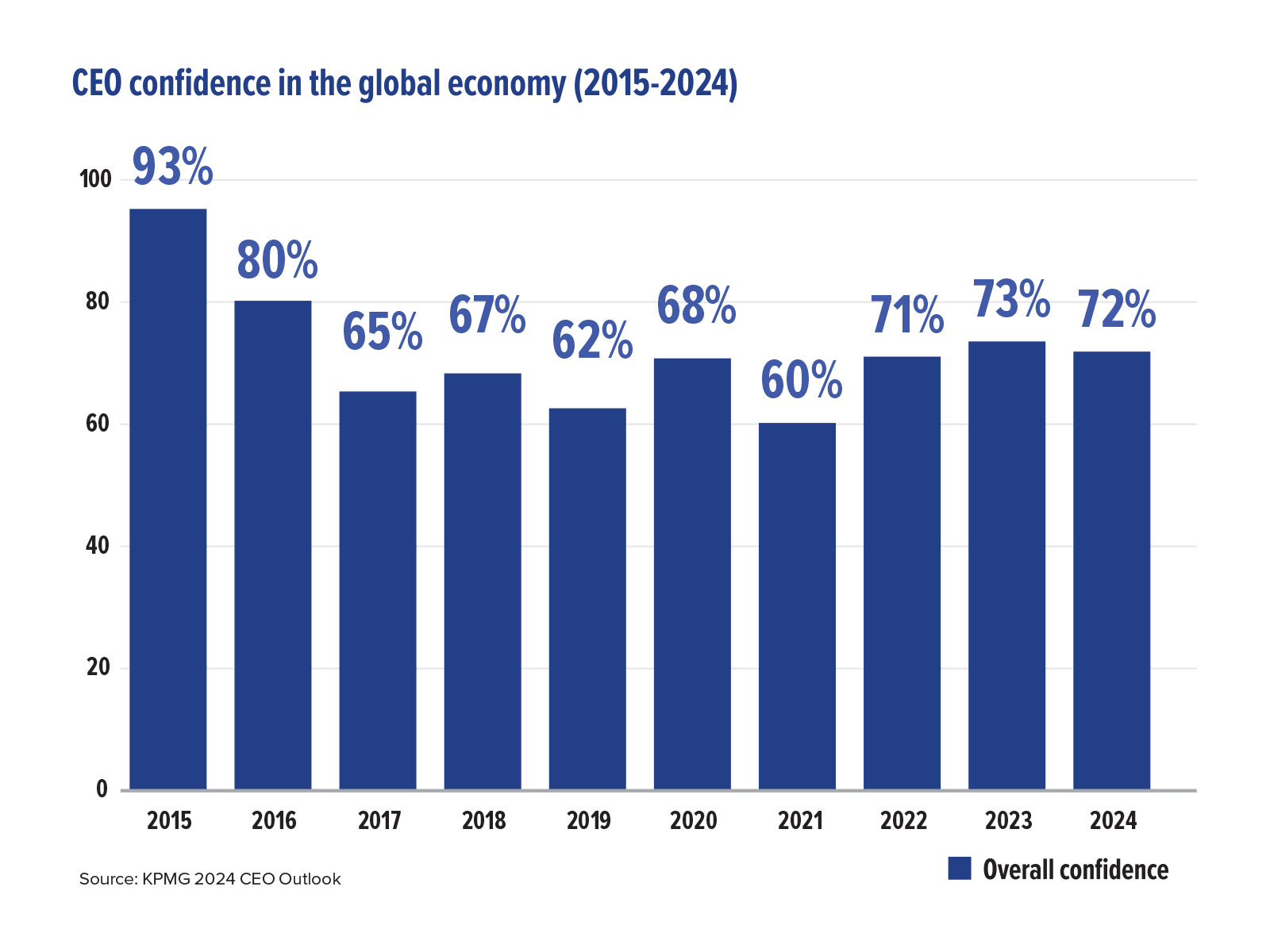
Down from 93% in 2015, CEO confidence in the global economy has remained relatively stable over the past three years, with this year’s survey showing that 72% of CEOs are optimistic about the economy. Still, due to the growing complexity and variety of demands of leading a large organization, almost three quarters of CEOs (72%) feel under more pressure to ensure the longterm prosperity of their business. This additional pressure could be attributed to an evolving list of threats to business growth, with supply chain disruption topping this year’s list, followed by operational issues and cybersecurity.
 CEOs have sought to create confidence in various ways, from increasing investment in innovation and tech to placing people at the heart of growth strategies and renewing their commitment to ESG and sustainability as a source of value creation. Respondents’ top operational priorities over the next three years are advancing digitization and connectivity across their business (18%), understanding and implementing generative AI across the business and upskilling their workforce (13%), and executing ESG initiatives (13%). By futureproofing their business for a digital world and focusing on fostering and retaining great talent, CEOs not only address their immediate operational needs but also position their organizations for sustainable, organic growth.
CEOs have sought to create confidence in various ways, from increasing investment in innovation and tech to placing people at the heart of growth strategies and renewing their commitment to ESG and sustainability as a source of value creation. Respondents’ top operational priorities over the next three years are advancing digitization and connectivity across their business (18%), understanding and implementing generative AI across the business and upskilling their workforce (13%), and executing ESG initiatives (13%). By futureproofing their business for a digital world and focusing on fostering and retaining great talent, CEOs not only address their immediate operational needs but also position their organizations for sustainable, organic growth.

Technology and Generative AI
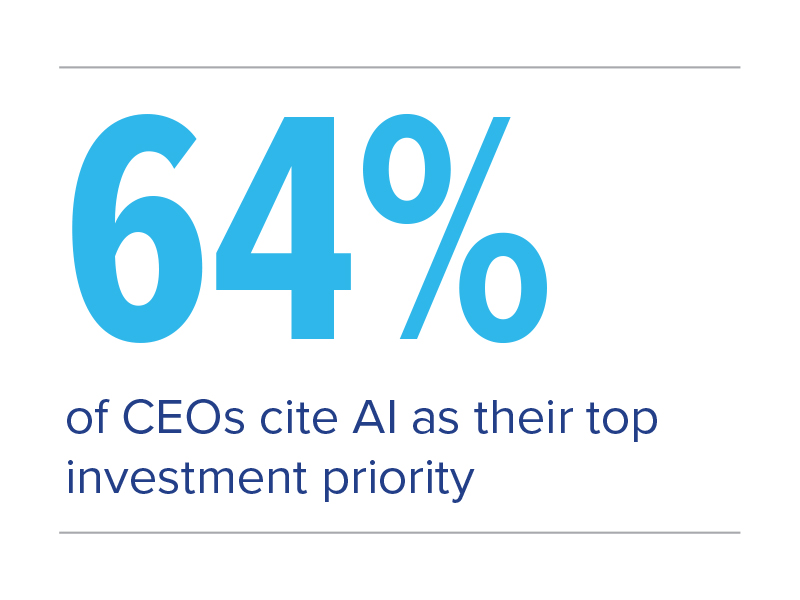
In 2024, leaders are reaffirming their commitment to increase investment in innovation and technology, including AI, as a driver of growth, with a majority (64%) identifying AI as their top investment priority. While CEOs recognize AI’s potential to increase efficiency and productivity, upskill the workforce for future readiness, and increase organizational innovation, they remain aware of the risks tied to rapid adoption. Well over half (61%) cited ethical challenges as some of the most difficult to address when implementing AI within their business, with lack of regulation (50%) and technical skills and capabilities (48%) also posing challenges.
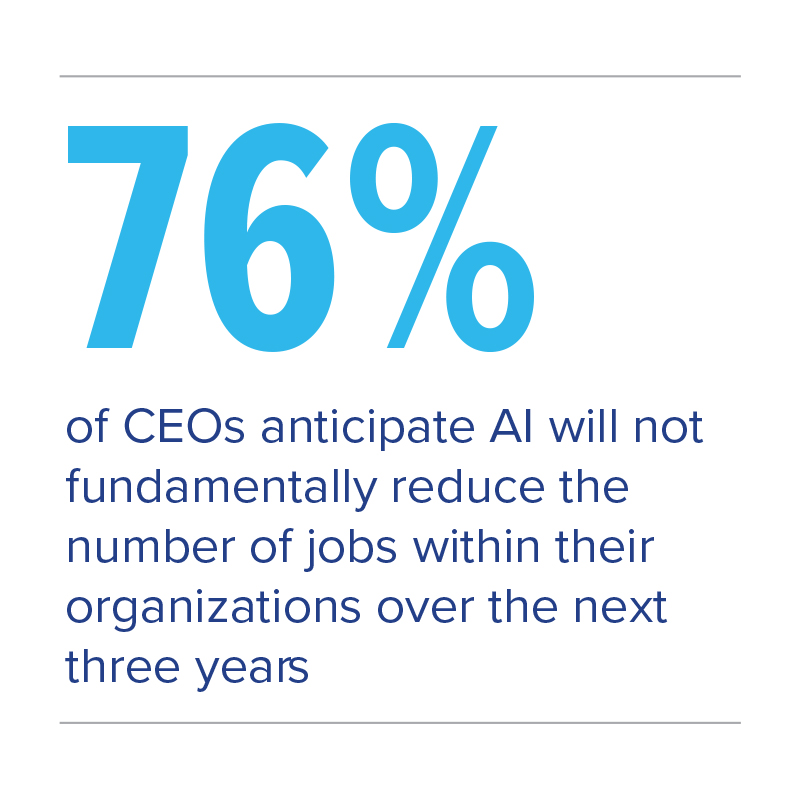
 Despite public concern around the risk of redundancies, CEOs remain confident that AI will not have a detrimental impact on the workforce, with over three quarters (76%) anticipating it will not fundamentally impact the number of jobs in their organization. Nonetheless, only 38% felt that their employees have the right skills to fully leverage the benefits of AI, and 58% agree that the integration of generative AI has made them rethink the skills required for entry-level roles.
Despite public concern around the risk of redundancies, CEOs remain confident that AI will not have a detrimental impact on the workforce, with over three quarters (76%) anticipating it will not fundamentally impact the number of jobs in their organization. Nonetheless, only 38% felt that their employees have the right skills to fully leverage the benefits of AI, and 58% agree that the integration of generative AI has made them rethink the skills required for entry-level roles.
Talent
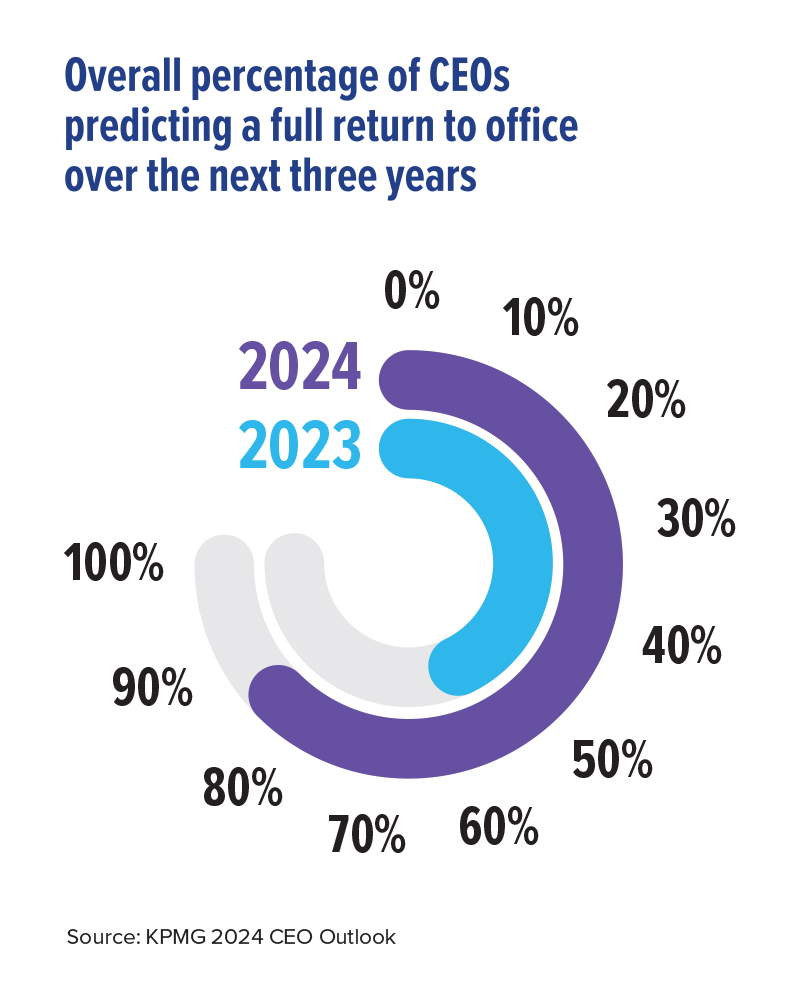
Since 2015, CEOs have grappled with shifts in working patterns as employees seek more balance, flexibility, and stronger alignment between personal beliefs and organizational purpose. Successful leaders are those who put people at the heart of their growth strategies and evolve their social contract to keep up with the evolving expectations of current and future talent. However, this year’s findings reveal that CEOs are hardening their stance on returning to pre-pandemic ways of working: 83% now expect a full return to office within the next three years (up from 64% in 2023), and 87% say they are likely to reward employees who make an effort to come into the office with favorable assignments, raises, or promotions.
 Regarding other talent-related issues that could affect future growth and competitiveness, 31% of CEOs say they are concerned about labor market shifts, specifically the number of employees that will soon retire and the lack of skilled workers to replace them. In response to a perceived talent shortage, 80% of CEOs agree that organizations should invest in skills development and lifelong learning within local communities to safeguard access to future talent, with 92% hoping this will help increase the overall headcount of their workforce over the next three years.
Regarding other talent-related issues that could affect future growth and competitiveness, 31% of CEOs say they are concerned about labor market shifts, specifically the number of employees that will soon retire and the lack of skilled workers to replace them. In response to a perceived talent shortage, 80% of CEOs agree that organizations should invest in skills development and lifelong learning within local communities to safeguard access to future talent, with 92% hoping this will help increase the overall headcount of their workforce over the next three years.
 ESG
ESG
With growing awareness, over the past decade, of ESG’s impact on trust and reputation, almost a quarter (24%) of CEOs acknowledged that the principal downside of failing to meet ESG expectations would be giving their competitors an edge, coming out ahead of threat to their own tenure (21%) and recruitment challenges (16%). Three quarters (76%) said they would be willing to divest a profitable part of the business that was damaging reputation, and 68% said they would take a stance on a politically or socially contentious issue, even if the Board raised concerns with them doing so. However, well over half (66%) of CEOs admit they are not prepared to withstand the potential shareholder scrutiny, and 69% said they have adapted the climate-related language and terminology used to meet changing stakeholder needs. Finally, 30% say the greatest barrier to achieving their climate ambitions is the complexity presented by the decarbonization of their supply chain, an issue further compounded by current geopolitical tensions around the world and activities impacting major global trade routes.
—
About the KPMG CEO Outlook
The 10th edition of the KPMG CEO Outlook was conducted between July 25 and August 29, 2024, with 1,325 CEOs overseeing companies with annual revenues over $500 million and a third of companies surveyed having more than $10 billion in annual revenue. The survey included CEOs from 11 key markets (Australia, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Italy, Japan, Spain, UK, and US) and 11 key industry sectors (asset management, automotive, banking, consumer and retail, energy, infrastructure, insurance, life sciences, manufacturing, technology, and telecommunications).